Comparative Evaluation of Adjunctive Oral Irrigation in Diabetes
Al-Mubarak S, Ciancio S, Aljada A, et al. J Clin Periodontol 2002; 29:295-300. Study conducted at the University of Buffalo, School of Dental Medicine.
Objective
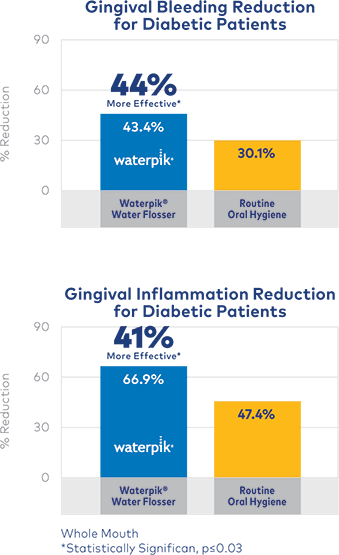
To compare the addition of the Waterpik™ Water Flosser with the Pik Pocket™ subgingival irrigation tip to routine oral hygiene on the periodontal health of people with diabetes.
Methodology
Fifty-two subjects with periodontal disease and either type 1 or type 2 diabetes participated in this three-month randomized clinical trial.
All subjects received scaling and root planing at baseline, then were assigned either to add a Waterpik Water Flosser with the Pik Pocket Tip twice daily to their oral-hygiene routine or to continue their regular routine.
Periodontal health was measured using both clinical and metabolic parameters.
Results
Adding the Waterpik Water Flosser was superior to normal oral hygiene in reducing the traditional measures of periodontal disease—plaque biofilm, gingivitis, and bleeding on probing.
The Waterpik Water Flosser also reduced serum levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and PGE₂, as well as reactive oxygen species—a bacteria- and host-mediated pathway for tissue destruction implicated in the pathogenesis of over one hundred conditions.
Conclusion
The Waterpik Water Flosser provided significant periodontal-health benefits, both clinically and biologically, to people with diabetes.