Waterpik® Water Flosser: Significantly More Effective than the Sonicare® Air Floss Pro for Improving Oral Health
Effectiveness of two Interdental Cleaning Devices on Clinical Signs of Inflammation: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Goyal CR, Lyle DM, Qaqish JG, Schuller R. A direct comparison of two interdental cleaning devices on clinical signs of inflammation: a four-week randomised controlled trial. Ann Clin J Dent health 2018;7:10-15.
Objective
To determine the effectiveness of a Waterpik® Water Flosser in reducing clinical signs of inflammation as compared to an air floss.
Methodology
Seventy subjects were randomized equally into two groups in this four week, parallel clinical trial: manual tooth brushing and water flosser (WF, model WP-120, two prong plug) or manual tooth brushing and air floss (AF, Model HX8340, two prong plug). Inflammation was measured using bleeding on probing (BOP) and the Modified Gingival Index (MGI) at baseline, two weeks, and four weeks. The Rustogi Modified Navy Plaque Index (RMNPI) scores were measured at baseline, two weeks, and four weeks. Both groups followed manufacturer instructions for use of interdental devices for one minute. The Waterpik® Water Flosser group used power setting eight and the Air Floss group used the three burst setting.
Results
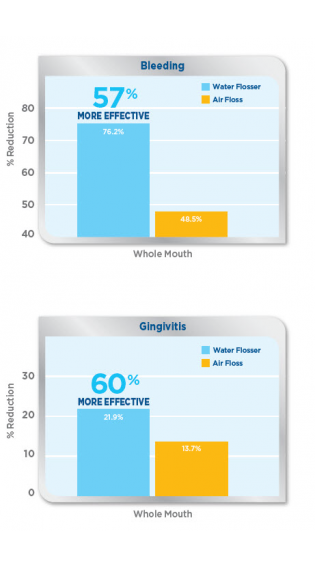
Both groups showed a significant reduction in BOP, MGI, and RMNPI at two weeks and four weeks (p<0.001). The Waterpik® Water Flosser was at least 50% more effective than the Air Floss at reducing BOP for all areas measured at 4-weeks (p<0-001). The Waterpik® Water Flosser was also more effective than the Air Floss for reducing MGI: 60% for whole mouth, 68% for proximal area, 86 for facial proximal area, 54% for lingual proximal area, 48% for marginal area, 62% for facial marginal, and 36% for lingual marginal area (p<0.001). The Waterpik® Water Flosser was more effective for reducing plaque compared to the AF for whole mouth (31%, P=0.008), proximal area (51%, p=0.017), and lingual surface (46%, p=0.004).
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that a Waterpik® Water Flosser and manual toothbrush are superior to the air floss and manual toothbrush in the reduction of inflammation and dental plaque.